 The Deepwave Digital v0.5.0 version of its Ubuntu-based AirStack SDR stack adds sampling rate and improved recovery support. AirStack runs on Deepwave’s AIR-T and with robust new AIR-T Edge systems based on the Jetson TX2i, Artix-7 FPGA and AD transceiver.
The Deepwave Digital v0.5.0 version of its Ubuntu-based AirStack SDR stack adds sampling rate and improved recovery support. AirStack runs on Deepwave’s AIR-T and with robust new AIR-T Edge systems based on the Jetson TX2i, Artix-7 FPGA and AD transceiver.
Philadelphia-based Deepwave Digital has released v.0.5.0 from its Ubuntu-based AirStack distribution for software-defined radio (SDR) applications. The software works on it AIR-T development boards and closed AIR-T embedded systems. Release 0.5.0 is required for the recently announced AIR-T Edge series. The original model AIR-T Edge AIR8201 is on pre-sale at an undisclosed price.
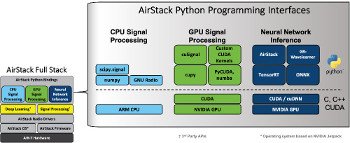
AirStack Architecture 0.5.0
(click on the image to enlarge it)
Like the AIR-T, the AIR-T Edge AIR8201 runs on Nvidia’s Jetson TX2i module along with Xilinx’s Artix-7 FPGA and Analog Devices’ 9371 RF transceiver. The new model adds rugged features, including upcoming IP56 protection. Other enhancements include improved frequency range, M.2 storage and an optional GPSDO (see below).
AirStack software and AIR-T (Artificial Radio-Transceiver) boards differ from most SDR solutions by adding in-depth training activated by APIs that take advantage of the graphics AI capabilities of Nvidia’s Jetson modules. All AIR-T systems, including Edge, use zero-copy memory access “to overcome the data transfer costs typically associated with GPU processing,” Deepwave said.

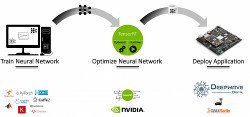
AIR-T Edge AIR8201 (left) and AirPack workflow
(click on images to enlarge)
The Jetson GPU allows AirStack to run parallel applications such as AI and signal processing directly on the RF sensor. “This reduces cost and complexity by eliminating the auxiliary computer required by most SDR vendors, and allows processing to be localized with the deployed radio without the need to stream data to a remote processor,” says Deepwave. AirStack comes with an optional AirPack designed to facilitate AIR-T’s TensorFlow RF training.
AirStack 0.5.0 provides “significant” performance improvements and API upgrades over earlier updates, Deepwave said. We reported in 2019. AirStack v0.2which added variable sampling rate, phase lock for MIMO and easier updates, among other features.
AirStack 0.5.0 adds support for continuously variable (CV) sampling rates activated by upgraded interpolation and decimation filters. The filters can be adjusted continuously between 3.9 and 125 MSPS. The feature only works with the new AIR-T Edge or AIR7201 version of the AIR-T with the more powerful Artix-7, which was released after the AIR7101 model we covered in 2019 (see below).
AirStack now supports multiple images of the Artix-7 FPGA firmware installed with the AirStack firmware to protect against unrecoverable board conditions during image loading. There is also improved open source support Konda package and environment management system. Conda, which is now upgraded here to Anaconda 4.10.3, adds support for GNU Radio, a major component of AirStack.
AirStack 0.5.0 upgrades to Ubuntu 18.04 with Linux 4.9, as well as Nvidia JetPack 4.6 (L4T 32.6.1) and CUDA 10.2. Other updates include TensorRT 8.01, cuDNN 8.2.1 and SoapySDR 0.8.
AIR-T Edge
Deepwave Digital’s new AIR-T Edge series starts with the AIR8201, which, like the newer version of the AIR7201 AIR-T built-in systems, progress to Artix 7 200T FPGA. The Artix 7 200T provides 215.3K logic cells (LUT), 740 DSP slices and 12.14 kbits of RAM. (Artix 7 75T of the original AIR7101 AIR-T system is limited to 75.5k LUTs, 180 slices and 3.75 Kbits.)

AIR-T Edge AIR8201 with (left) and without cover
(click on the image to enlarge it)
Like the AIR-T systems, the AIR-T Edge series is only available in development boards or in closed models, and for the first time the latter can be safely placed outdoors. Like other AIR-T systems, the new model allows SDR applications to process bands greater than 200 MHz in real time, Deepwave said.
The AIR-T Edge AIR8201 offers the same Jetson TX2i module, the durable, 10-year lifecycle of the six-core TX2, which in terms of performance falls between the Jetson Nano and Jetson Xavier NX. It also provides analog devices 9371 RF transceiver with 2 × 2 MIMO. The transceiver provides 100MHz dual-channel transmission and reception. (The second receiver requires an additional daughter card.)


AIR-T Edge AIR8201 motherboard (left) and AIR-T Embedded AIR7201
(click on images to enlarge)
Compared to the AIR7201, the AIR8201 adds internal integration to the GPSDO (GPS Disciplinary Oscillator) module. The new model also offers improved receiver performance, including an extended frequency range from 30MHz to 6GHz (vs. 300MHz to 6GHz). There is also an additional 28 dB gain when receiving for 36 dB plus 2.2 dB figure noise.
Compared to the supplied versions of the AIR-T systems, the AIR-T Edge AIR8201 provides more extensive features for robust processing. They include an operating range of -40 to 85 ° C (compared to 0 to 70 ° C) with a 95% relative humidity tolerance at -10 to 65 ° C (no condensation). The housings also add 5Grms vibration and 140G impact resistance. The case is expected to be certified for IP56 protection.
The main new addition to the AIR8201 interface is the M.2 SATA storage slot. It is not clear whether this replaces the earlier SATA interface. There is now a microSD slot in place of the SD slot
Like earlier models, the AIR-T Edge is additionally equipped with GbE, USB 3.0, USB OTG and 4K-ready HDMI ports. The system works with a maximum of 25W. The full specifications have not yet been published in AIR-T wiki, but the image shows a serial port and an expansion connector, which is probably used for the previously available DIO.
Probably on board are the previous WiFi / BT radio, external LO input, PPS, 10MHz reference input and 8-15VDC input. The PCB seems to retain the earlier Mini-ITX form factor.
More information
AirStack 0.5.0 is now available for download to Deepwave Digital customers. AIR-T Edge AIR8201 is available for pre-sale at an undisclosed price. (The original AIR-T boxless board was available for $ 4,995 from Crowd Supply.)
More information can be found at Deepwave’s AirStack 0.5.0 messageas well as his AIR-T Edge message and AIR-T Edge product page.
